Virtual events: potential for the music industry?
Virtual technologies are bringing real-life live event experiences into the home for the first time, enabling feeling of real co-presence for shared experiences for people living remotely. This results in numerous new opportunities to deliver music-based content and provide artists with direct, low-resource access to the target audience.
A new technology to meet user needs
Virtual events as a new digital medium, combining resource efficiency and availability with a high experiential component and social presence.
The success of digital media is based on their high accessibility and availability while fulfilling basic needs such as entertainment and social participation. Their use fits perfectly into our everyday life. For example, we spend a lot of time during the day consuming digital media and socializing via telecommunications applications. Real experiences, such as attending concerts or festivals, on the other hand, create unforgettable experiences and are characterized by a special social component. A communal experience and direct social exchange create shared memories connect. Thus, 40% of the population attends 1 to 2 concerts per year [1]. However, participation in real events is often associated with a very high level of effort. Beside an effort of resources (time and money), the low regional availability of desired events and the difficulty of planning joint visits often stand in the way of using these offers. This also shows that only 10% of the population regularly attend concerts or similar events [1].
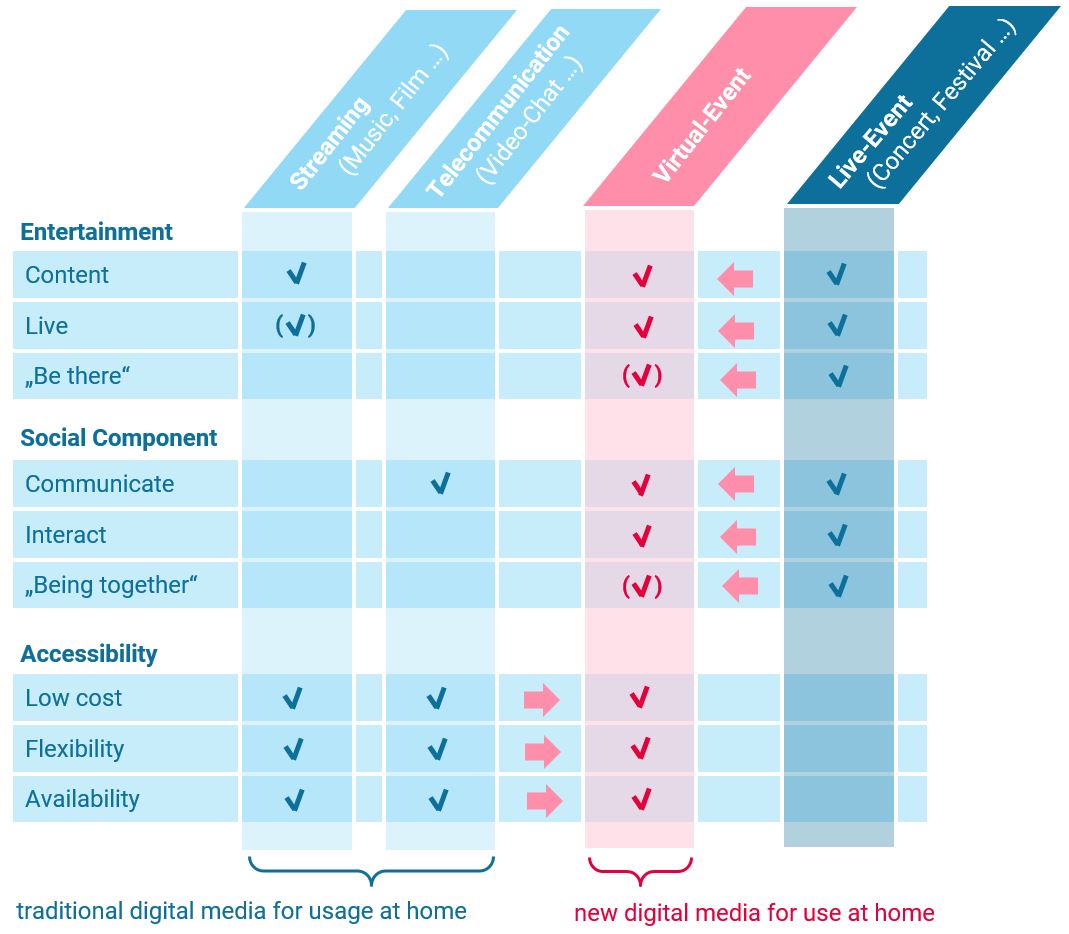
Virtual events as a new form of meeting user needs in terms of different forms of social and cultural participation
Reasons for not attending live events
The focus is on the high time and financial costs involved. This also includes infrastructural conditions and geographical circumstances, which are associated with corresponding travel expenses [2]. Since live events are social events that are rarely consumed alone, there is also the need for social companions who must also share the same interests in relation to the artistic content. In practice, their existence and temporal availability is often associated with limitations.
Reasons for attending live events
The experience component is decisive for attending real events. The „authenticity“ of the concert and the atmosphere are important reasons for attending [3]. As a social event, live events primarily address needs for social exchange and interaction and the sharing of common interests. Other factors are the proximity to the artist and the sense of community of the group experience.
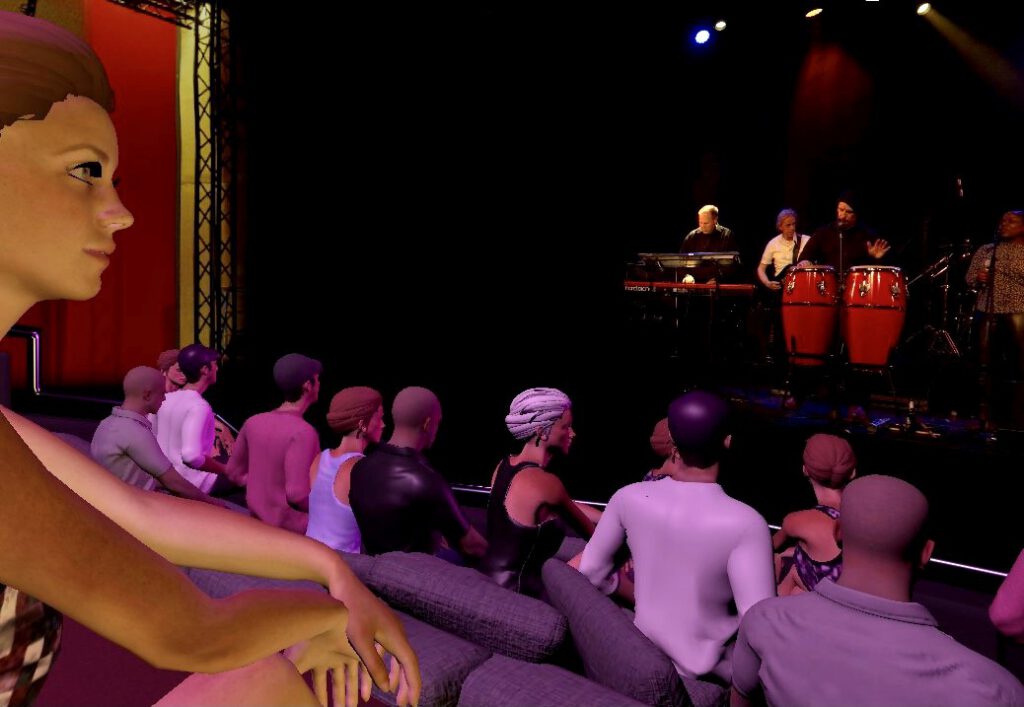

The visual and auditory immersion as well as one's own embodiment in the virtual environment are special prerequisites for Place Illusion
Virtual technologies offer the potential to combine the advantages of digital media use and real events and to make the experience of a real-physical experience and social interaction usable at home under the premise of a low use of resources and suitability for everyday use. This makes it possible for me to spontaneously attend a concert of our favorite band in Rome from Berlin with my girlfriend, who lives in Paris. The experience doesn’t copy reality, but the immersion of the virtual space can still create the feeling of being there, and the social presence illusion of my girlfriend, mediated by a lifelike avatar, creates the feeling of real co-presence and togetherness. This makes it possible to reach target groups that were previously prevented from attending physical events. After all, this includes around 60% of the total population [1, 4].
The virtual event as a new direct distribution channel for artists
Virtual reality can create the feeling of being spatially with distant people.
Despite lower usage figures, music events generate the largest revenues in the music industry, which proves the high added value of experience-based formats from the customer’s point of view in terms of willingness to pay. Artists benefit from this only to a limited extent. Although artists‘ revenues are generated predominantly from live performances, the live event format is particularly personnel-intensive and many trades and market players earn a share from it. In addition, the planning and execution of concerts and tours is very resource-intensive. Real-physical restrictions prevent the scalability of such events. For example, real venues have limited space and not all venues offer a good view. The regional accessibility of such venues also ensures a limited reach. In order to reach a large number of people, therefore, corresponding tours are necessary, which entail high costs. An additional long-term risk is the decline in attendance even before the Corona pandemic [5]. Moreover, the consequences of the long pandemic experience on consumer behavior are not foreseeable.
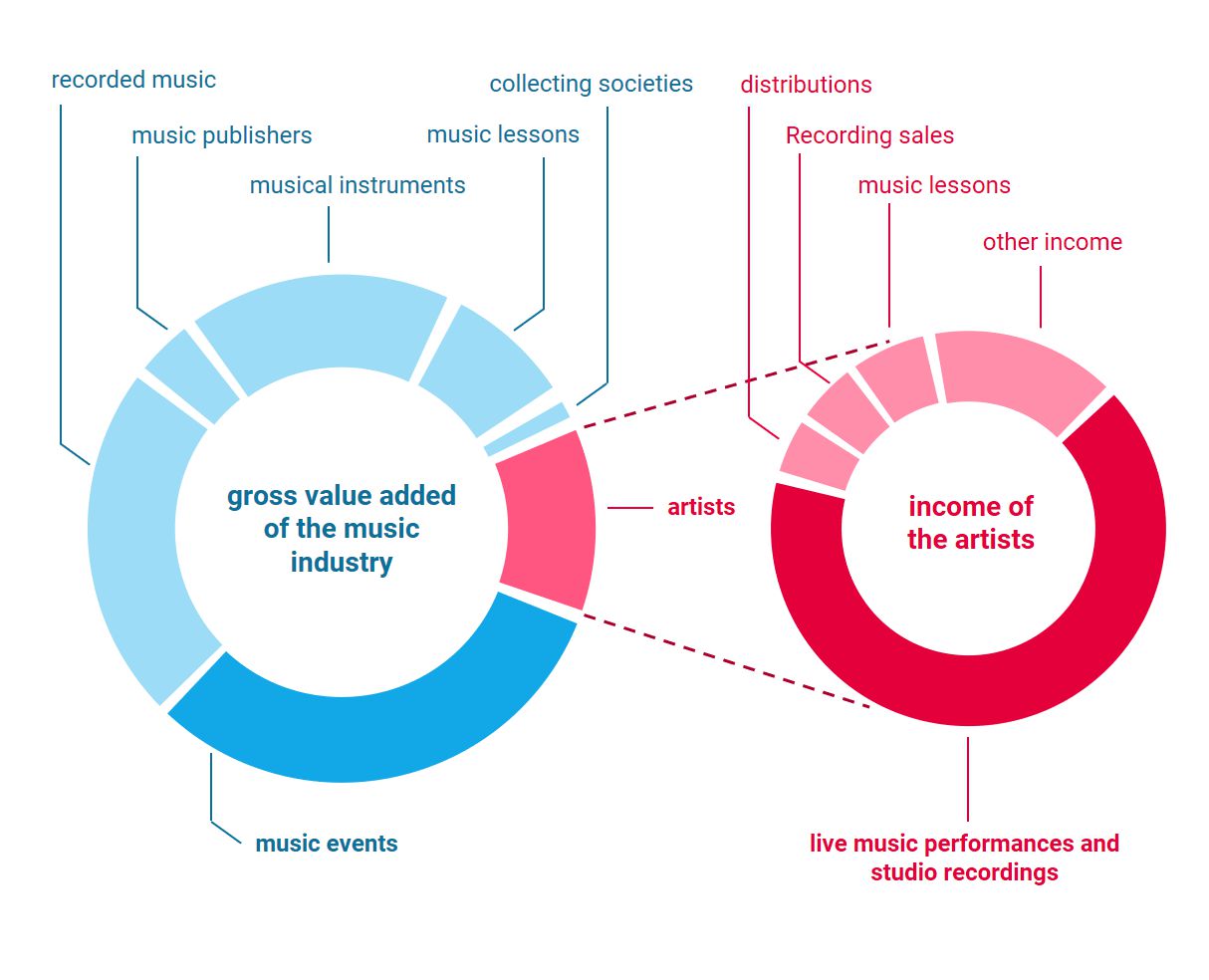
Share of music events in the value added of the music industry and sources of income for artists: While music events generate the largest turnover in the music market and represent the main source of income for artists, artists only profit to a subordinate extent from the value added that has arisen.
Virtual events can strengthen the market position of artists and open up new ways of monetizing their content. Streaming real performances into virtual spaces enables audience scaling at comparatively low cost. Virtual events can serve as a supplement to, but also as a substitute for, real live performances, for example for artists with limited resources or in pandemic situations. Significantly lower ticket prices could encourage more people to attend more often and allow artists to earn higher margins. Possibilities of actively controlling the atmosphere of virtual events – although 1000s of participants will virtually visualize only a small exclusive concert or vice versa – as well as design detached from real-physical laws offer completely new approaches to stage artistic content.
Scenario 1: Streaming a live concert
Streaming a real-physical live performance into a virtual event space can expand the audience without incurring significant additional costs. Scaling is achieved and the reach of a local event is opened to visitors from all over the world.
Advantages:
- Reaching people who cannot participate in the real event
- Generation of additional revenue
- Hardly any additional effort and costs
Scenario 2: Virtual concert
Purely virtual concerts allow artists to perform additional shows for an exclusively virtual audience. This eliminates all the time and financial costs associated with real events and tours. Especially artists with a small fan base can benefit from this. But high flexibility and efficiency also offer great advantages for established artists.
Advantages:
- Supplement or substitute for real performances and tours
- Significantly lower costs with simultaneously high reach
- Hardly any time and organizational effort
- new possibilities of presentation of artistic content
Scenario 3: New kind social medium
The feeling of being there and genuine co-presence also opens up new possibilities for interaction between artist and audience. With the perceived proximity of the audience to the artist, new added values can be achieved despite the real spatial distance.
Advantages:
- Feeling of closeness to the artist, without negative effects of real physical proximity
- New forms of social participation of the fanbase in the artist’s content
[1] BDKV (2020): Musikwirtschaft in Deutschland 2020. Studie zur volkswirtschaftlichen Bedeutung von Musikunternehmen unter Berücksichtigung aller Teilsektoren und Ausstrahlungseffekte.
[2] Dollase, R. (1997). Musikpräferenzen und Musikgeschmack Jugendlicher. In: Baacke, D. (eds) Handbuch Jugend und Musik. VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften, Wiesbaden.
[3] Schneider, Damman, Kleist (2008): Live-Musik-Publikum in Hamburg. Empirische Studien zu einer urbanen Musik-Szene im digitalen Zeitalter. LIT Verlag.
[4] statistica (2021): Anzahl der Personen in Deutschland, die Musikveranstaltungen oder Konzerte besuchen, nach Häufigkeit von 2017 bis 2021
[5] GfK (2018): Live Entertainment Deutschland. Eine Studie des Bundesverbands der Veranstaltungswirtschaft (bdv), durchgeführt von der Gesellschaft für Konsumforschung (GfK).
